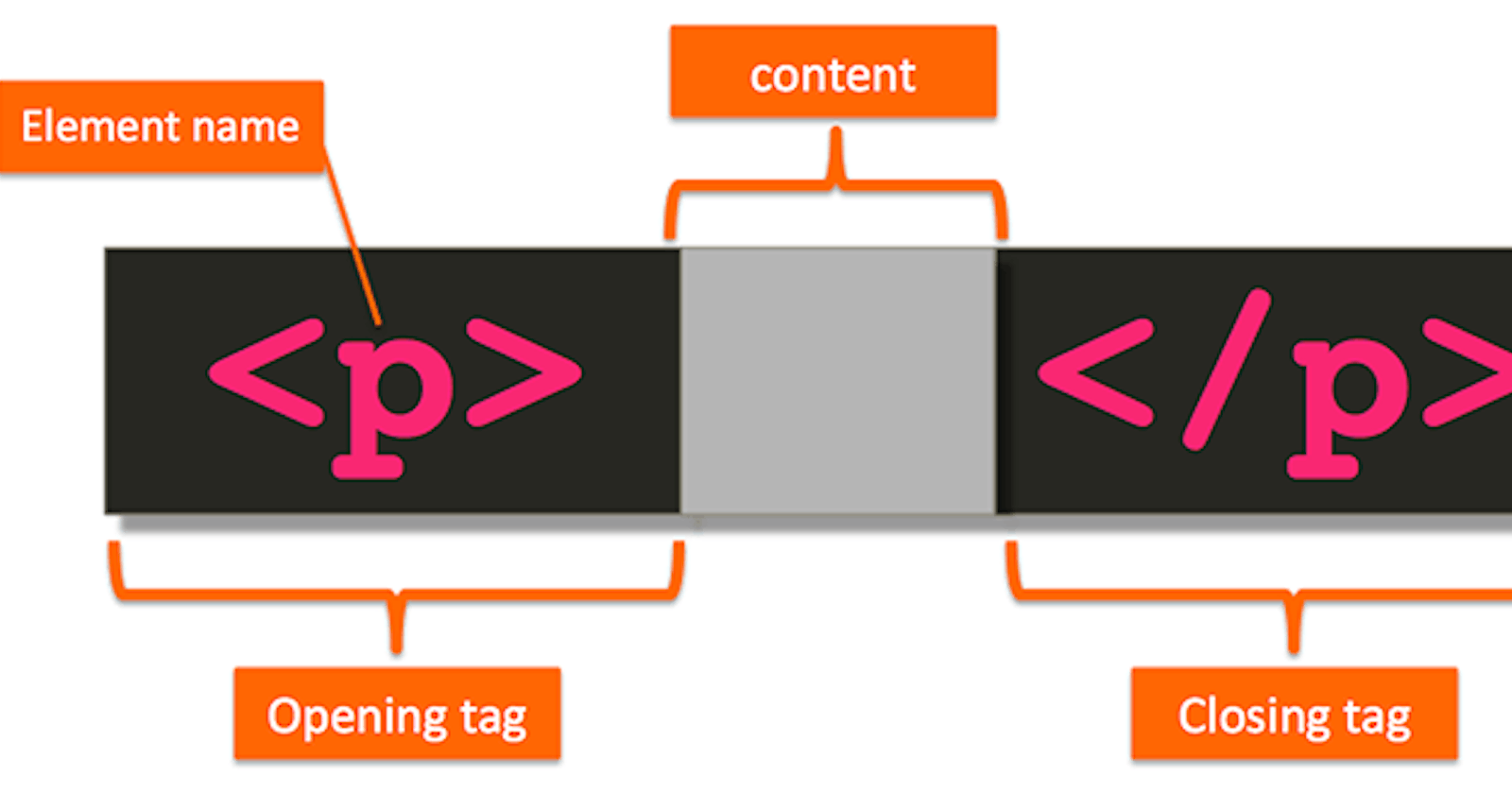
Usually, an HTML tag consists of an opening and a closing tag that surrounds some content as shown in below :
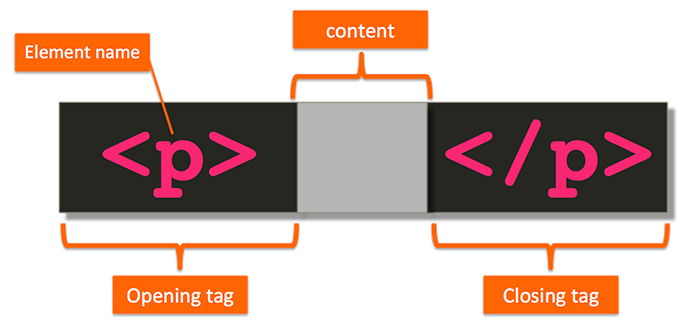 In this case, the tag
In this case, the tag <p>, which stands for paragraph, is communicating us that the content in the gray area should be treated as a paragraph.
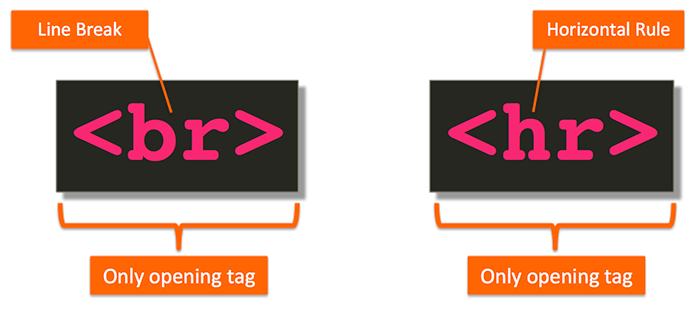
Most HTML tags have a closing tag.
Most HTML tags have a closing tag. However, not all of them do. For example, as shown below, the <br> and <hr> tags only have an opening tag (br stands for line break, and hr stands for horizontal rule). They don’t have a closing tag at all.
 In fact, the following code snippet would be invalid HTML :
In fact, the following code snippet would be invalid HTML :
<br>Hello World!</br>
The reason? The <br> tag tells the browser to create a line break in text, i.e., anything that comes after the <br> tag should be displayed on the next line. It would never make sense for the <br> tag to surround some content and therefore it’s not allowed to.
Here Self-closing Tag Comes into the picture.
If you have come from the world of XML or XHTML, you may have heard of the concept of a self-closing tag. So, let dig it in.
What is Self-closing tag?
Some HTML tags don't have their own content. These are known as self-closing tags or empty tags. Self-closing tag looks like <tag />.
In XML and XHTML, a self-closing tag is a shorthand notation for an opening and closing tag in one. It’s used to communicate lack of content in between the opening and closing tags. It combines the beginning and end.
<br /> = <br> + </br>
In practice, </br> does not exist. Just <br> or <br />
In XML, any tag can be self closing. however, with HTML, only tags which are defined as such should be used that way. So you should never do <div />, instead you should use <div></div>, even if it's empty.
You can view the full list of self-closing tags here